Gout
Last reviewed by Dr.Mary on August 7th, 2018.
What is Gout?
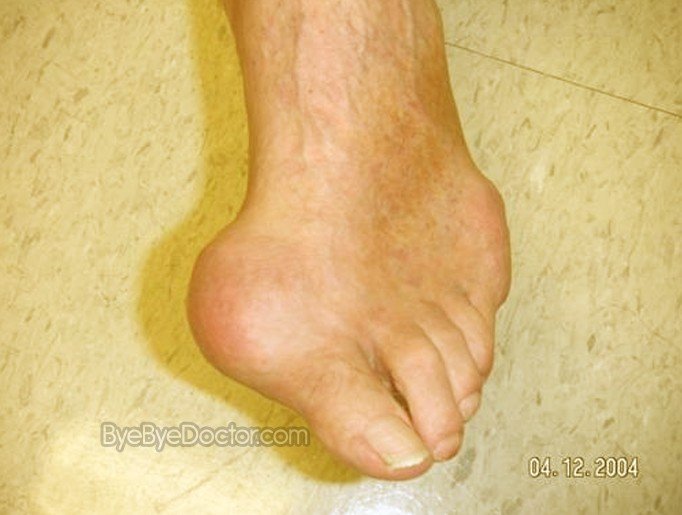
This is intricate type of arthritis categorized by very sudden and severe bouts of redness, tenderness, as well as pain in joints, especially the joint which is at the point on the foot where the large toe begins. This attack normally occurs when uric acid builds in the joints.
Gout may affect anyone – both male and female. Males are somewhat more probable to have gout but females are increasingly vulnerable to developing gout after menopause.
The usual acute bout of gout may wake the individual in the night with the sensation of the big toe being set on fire. The joint which is affected is swollen, hot and so very tender that a bed sheet’s weight on the toe can be almost unbearable.
Luckily, gout is correctable, and there are also methods to decrease the threat of gout recurring.
Gout Symptoms
The symptoms and signs of an attack of gout are at all times serious, taking place very suddenly – regularly at night – and lacking any warning. These symptoms include:
Joint pain that is intense
Gout normally distresses the big joint of the large toe however it also can happen in your ankles, feet, knees, wrists and hands. This pain is probable to be at the peak severity for the first twelve to twenty-four hours after beginning.
Redness and inflammation
The affected joint or joints will be swollen, red as well as tender
Discomfort which is lingering
After the severe pain decreases, some joint uneasiness can last from several days to several weeks. Future attacks are usually probable to last much longer and to affect many more joints.
If an individual experiences intense, sudden pain in a joint, the primary care physician should be called. Gout which it not treated can cause worsening pain as well as joint damage.
If the individual also has fever as well as a joint which is inflamed and hot, these are signs of an infection and medical care should be sought immediately.
Gout Causes
Gout happens because of a buildup of urate crystals around the joint, and causes inflammation as well as the extreme pain of an attack of gout. Urate crystals form because there are high points of uric acid in the blood. The human body creates uric acid when it breaks down purines – substances which are found in the body naturally – as well as in definite foods such as organ meats, anchovies, herring, mushrooms and asparagus.
Usually, uric acid will just dissolve in the blood and pass thru the kidneys into the urine. But there are times when the body either creates too much uric acid or the kidneys expel too little uric acid. Whenever this occurs, uric acid accumulates, creating needle-like, sharp urate crystals in a joint or the tissue surrounding the joint and causes swelling, inflammation, and of course, intense pain.
An individual is most likely to have gout when they have high levels of uric acid in the body. Features which raise the level of uric acid in the body include:
Factors of lifestyle
Choices which you create in normal everyday life can increase the hazard of gout. Unnecessary use of alcohol – usually more than 2 drinks each day for men and beyond 1 drink for women – can increase the hazard of gout.
Medical problems
There are certain conditions and diseases which raise the risk of gout developing. These are high blood pressure left not treated or hypertension, and enduring diseases such as diabetes, levels which are high of cholesterol and fat in the blood system or hyperlipidemia as well as the narrowing of arteries or arteriosclerosis.
Some medications
Using thiazide diuretics – frequently prescribed for the treatment of high blood pressure – and aspirin in low-dosage likewise can cause the levels of uric acid to increase. So can using drugs for anti-rejection prescribed for individuals who have experienced an organ transplant.
History in family of gout
If any additional family members of the individual’s have had gout, then the individual is likely to also develop the illness.
Sex and age
Gout happens most frequently in men than in women, mainly since women have a tendency to have a lesser uric acid point than men do. Following menopause, however, women’s uric acid levels start to approach levels of men. Males as well are more likely to develop gout earlier in life – generally between the ages of 40 and 50 – while women normally develop symptoms and signs of gout after menopause.
Individuals with gout may have more-serious disorders, such as:
Gout which is recurrent
Many people may not ever experience gout symptoms and signs for a second time. But others can experience gout numerous times in a year. Medicines can help prevent attacks of gout in those with recurring gout.
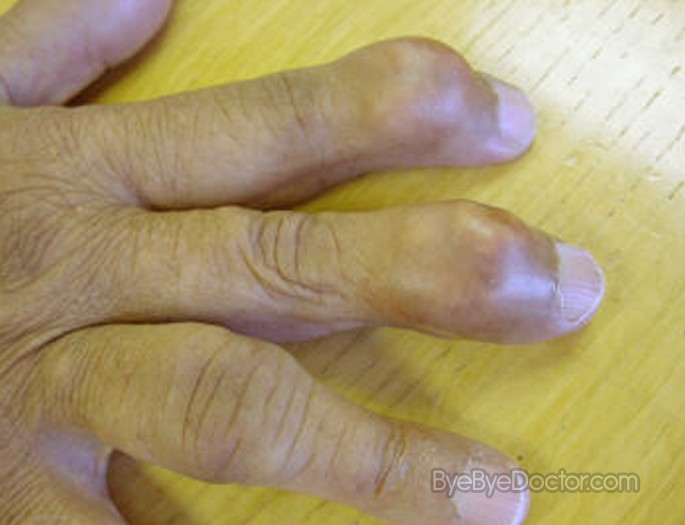
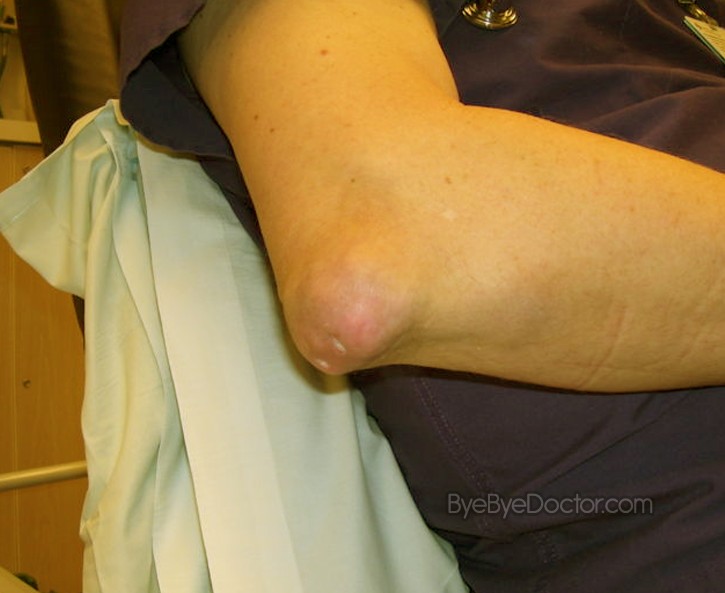
Gout which is advanced
Gout which is untreated can form urate crystals deposits beneath the skin in nodes called tophi. Tophi normally are not painful but can become tender and swollen during bouts of gout.
Kidney stones
Urate crystals which collects in the urinary tract, causes kidney stones. Medicines can assist in reducing the probability of this problem. .
Gout Treatment
The primary care physician will order lab work to aid in making the diagnosis of gout and these tests can include:
Fluid in joint
The physician will draw fluid using a needle from the joint which is affected. It will be observed under a microscope where the joint fluid can expose urate crystals.
Blood test
The physician may also suggest a blood test to measure the level of uric acid in the blood. Blood test results can often be misleading. Some individuals have high uric acid levels but never suffer with gout. And other individuals have symptoms and signs of gout, but do not have an unusual level in the blood of uric acid.
Gout treatment normally includes drugs. What medicines that will be used are based on the individual’s health as well as individual preferences.
Different drugs are recommended to:
- Treat serious bouts of gout as well as avert attacks in the future.
- Decrease any danger of complications from gout, for instants the urate crystals deposits which causes nodes to develop beneath the skin.
Drugs to manage attacks which are acute and avoid any attacks in the future consist of:
NSAID’s
NSAIDs or “non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs” can manage inflammation as well as pain in individuals who suffer from gout. The primary care physician can prescribe a much larger dosage to halt an attack which is underway, then a much lesser daily dosage to prevent any attacks in the future.
NSAIDs comprise several selections over the counter for instance ibuprofen (Motrin, Advil) and naproxen as well as other powerful NSAIDs for example indomethacin (Indocin). Many NSAIDs bring a risk of bleeding, ulcers and pains in the stomach.
Colchicine
If the individual is not able to tolerate NSAIDs, the physician can recommend colchicine, which is a kind of pain medication which effectively reduces the pain of gout – particularly when begun quickly after indications appear. The effectiveness of this drug is countered in many cases by unbearable side effects for instance vomiting, diarrhea and nausea.
Following an acute attack of gout being resolved, the doctor can counsel to take colchicine in a lower daily dosage to stop any attacks in the future.
Corticosteroids
These types of drugs, for example the medicine prednisone, can control gout pain and inflammation. Corticosteroids can be managed in tablet form or can be given as an injection in the joint. Drugs like corticosteroids are commonly used on individuals who cannot take either colchicine or NSAIDs.
Corticosteroids side effects can include slow healing of wounds, thinning bones, as well as a reduced capability to fight any infection. To decrease the threat of these grim side effects, the physician will attempt to discover the dosage which is lowest that controls the symptoms as well as advice steroids use for the least time possible.
Medications used to stop the complications linked with numerous attacks of gout include:
Drugs that block the production of uric acid
These are known as “xanthine oxidase inhibitors” and include allopurinol (Aloprim, Zyloprim), as well as febuxostat (Uloric). They limit the uric acid amount that the body produces. This can lower the blood level of uric acid as well as reduce the gout risk. Allopurinol side effects comprise a low blood count as well as rash. Side effects of febuxostat are nausea, rash, and liver function which are reduced.
“Xanthine oxidase inhibitors” can cause a new, severe bout if taken prior to a current attack being completely subsided. By taking a short course of low-dosage colchicine before starting a “xanthine oxidase inhibitor” this risk can be decreased markedly.
Drugs that increases the removal of uric acid
Probenecid (Probalan) increases the kidneys’ capability to eliminate uric acid from the body. This can lower the levels of uric acid as well as decrease the threat of gout – the uric acid level in urine is enlarged. Probenecid side effects comprise a rash, kidney stones, and stomach pain.
Gout Diet
Gout has been linked to diet for eons, especially diets which cut down on alcohol, meats, and seafood. Because of this reason, treatment for gout used to have severe diet restrictions – so severe that it was very difficult to stay with the diet. Because of newer drugs for the treatment of gout, the necessity for this strict diet has been reduced.
To follow a gout diet, include the following:
Limit protein from animals
Animal protein should be limited to four to six ounces each day.
Eat more protein which is plant-based
This can be done by increasing legumes and beans.
Avoid or limit alcohol
The reason for this is that alcohol hinders the removal of uric acid from the body. If your gout is under control, you can drink one or two 5-ounce servings each day of wine which will more than likely not increase any risk for gout.
Drink lots of fluids
Drink lots of fluids, preferable water. Try for eight to sixteen 8-ounce glasses each day.
Choose fat –free or low-fat dairy products
These include low fat or skim milk as well as eating foods for example yogurt. Set a goal of 16 -24 fluid ounces each day.
More carbohydrates that are complex
This includes eating whole grains, fruits as well as vegetables with fewer carbohydrates which are refined such as candy, cakes and white bread.
Avoid or limit sugar
Eating too much sweets leaves no room for low-fat or fat-free dairy products and plant-based proteins. Foods full of sugar also tend to be high calories so most people will eat more than is likely to be burned off.
There is recent evidence that for men to drink 4 to 6 cups of coffee each day, can lower gout risk.
The results of following this diet will help limit the body’s production of uric acid as well as increase its removal. But it is not probable to lower uric acid enough to go without medication.